Dominance

In complete dominance, the dominant allele completely masks the effect of the recessive allele.
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.
The previous tutorial investigated Gregor Mendel and how he found trends in the phenotypes of offspring produced by true-breeding parents
Dominant and Recessive Alleles
Mendel paved the way to discovering that alleles that code for a particular characteristic, such as the shape of the seeds produced are expressed in dominant and recessive genes.
When dominant genes were present, they would supersede the presence of wrinkled and were deemed the dominant gene. For example;
If the genotype for seeds was Rr (where R is dominant and r is recessive), R would supersede the recessive gene and the plant would express a round seed phenotype.
If the genotype was rr (where both are recessive) there are no dominant genes, therefore, the recessive phenotype for wrinkled seed is expressed
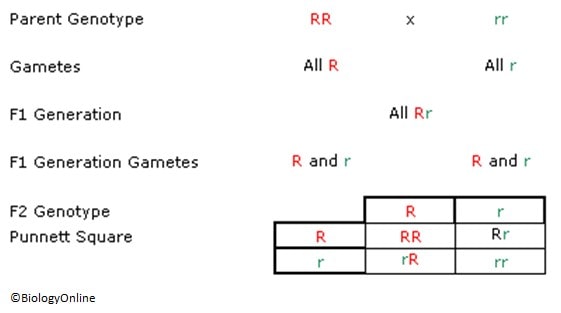
The previous tutorial mentioned that in the first generation all offspring produced were round seeds, and in the second generation for every three that were round seeded there would be one wrinkled seed. This can be expressed in a Punnett square as illustrated below.
tgenvideo
All dominant genes are marked in red, and all recessive genes are marked in green. Whenever the dominant gene is present in an organism this will be expressed. We can summarise the above diagram in the following statements
- Parent 1 possesses 2 dominant genes in its genotype
- Parent 2 possesses 2 recessive genes in its genotype
- The gametes produced by parent 1 all contain the dominant gene while parent 2’s gametes all possess the recessive gene.
- When parent 1 and 2’s gametes are crossed, the genotype is Rr. Since all of them have the dominant gene passed on from parent 1, they all express the dominant phenotype
- The gametes from the first generation produce 50% R gametes and 50% r gametes
- The second generation produces 1 RR 2 Rr and 1 rr genotypes in offspring, resulting in 3 round seed phenotypes per 1 wrinkled seed
This is an example of a monohybrid cross, where we are studying one respect of an animal’s genotype. The next tutorial continues to look at Mendel’s “law of dominance”.

|
GREGOR MENDEL & INHERITANCE WORKSHEET
This two-paged worksheet can be used to probe the student’s understanding of Gregor Mendel’s experiments on inheritance. This worksheet includes arranging text block and flowchart order, multiple choice, and Punnett Square exercises. Subjects: Genetics & Evolution |
You will also like...

Chemical Composition of the Body
The body is comprised of different elements with hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen as the major four. This tutorial..

Geological Periods
Geological periods is a study guide that cites the different geological periods on Earth's timeline. Each has a brief ov..

Growth and Plant Hormones
Plants, like animals, produce hormones to regulate plant activities, including growth. They need these hormones to respo..

Plant Water Regulation
Plants need to regulate water in order to stay upright and structurally stable. Find out the different evolutionary adap..

The Hominids
The hominid family diversified from the apes around 6 to 8 million years ago. Since then, the evolutionary path has prov..

Plant Biology
Plantlife can be studied at a variety of levels, from the molecular, genetic and biochemical level through organelles, c..
